Radiomics of Cervical Cancer
Project Summary:
According to the latest world cancer report published in 2014, cervical cancer is the third most common cancer with high incidence rate (0.14‰) and the fourth most common cause of cancer death with high mortality rate (0.068‰) among women in worldwide in 2012. It is the most common cancer among women in 39 of the 184 countries worldwide, and is the leading cause of cancer death in women in 45 countries. And it seriously affects life quality of women and threatens their lives. Therefore the accurate diagnosis and prognosis evaluation are intensely important for planning the individualized treatment for the cervical cancer victims.
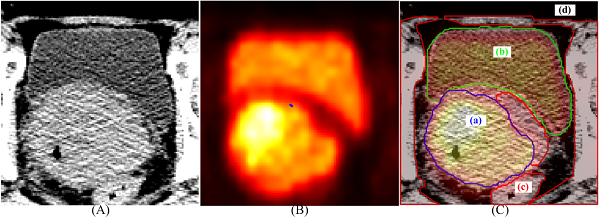
Figure 1(A) Part of the original CT images (B) Part of the original PET images (C) The corresponding fusion images
Recently, radiomics, which aims to convert medical images into high-dimensional data that reflects pathophysiology, has emerged and became a promising approach in the discovery of diagnostic and prognostic image based biomarkers. Some previous study has shown that radiomics features based on CT scans could provide valuable information in the accurate diagnosis and prognosis evaluation. With the popularity of PET/CT, radiomics based on PET/CT images have attracted more attention. Compared to single modality images, PET/CT images can provide metabolic and anatomical information at the same time. And a number of studies use image-derived features from both patients’ PET images and CT images to improve prediction results. Unfortunately, only a few of them investigate the importance of the fusion images. In our study, besides of taking PET or CT images alone, we also extract features from the PET/CT fusion images, which we believe provides more information, and related these quantitative descriptors for accurate diagnosis and prognosis prediction.
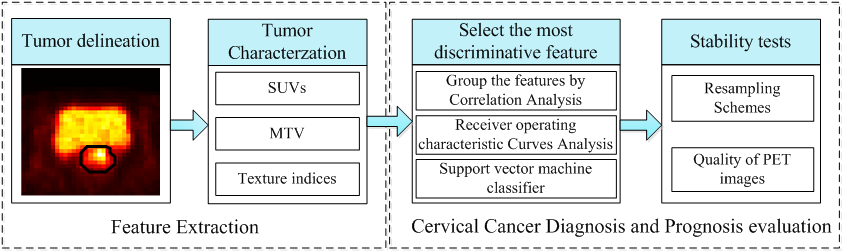
Procedure of Radiomics Analysis
Project Members
Post-Doc Fellow
Post-Doc Fellow
Applied Research Scientist
